The DGAC, Directorate General of Civil Aviation, is responsible for ensuring the safety and security of air transport. It is also a provider of air traffic services for airlines and general aviation. One of these services is aimed at guiding pilots in the safe landing of their planes using the ILS. Often making visual flight impossible, weather conditions are one of the key factors that favored the creation of this system.
The ILS (Instrument Landing System) is an instrument landing aid system with lateral (in the runway axis) and vertical (on the descent plane of the procedure) guidance. It ensures planes to land safely and in all weathers by transmitting guidance information via VHF.
This radioelectric aid thus provides pilots with information on site (glide path: glide path beacon) and in direction (localizer: runway alignment beacon).
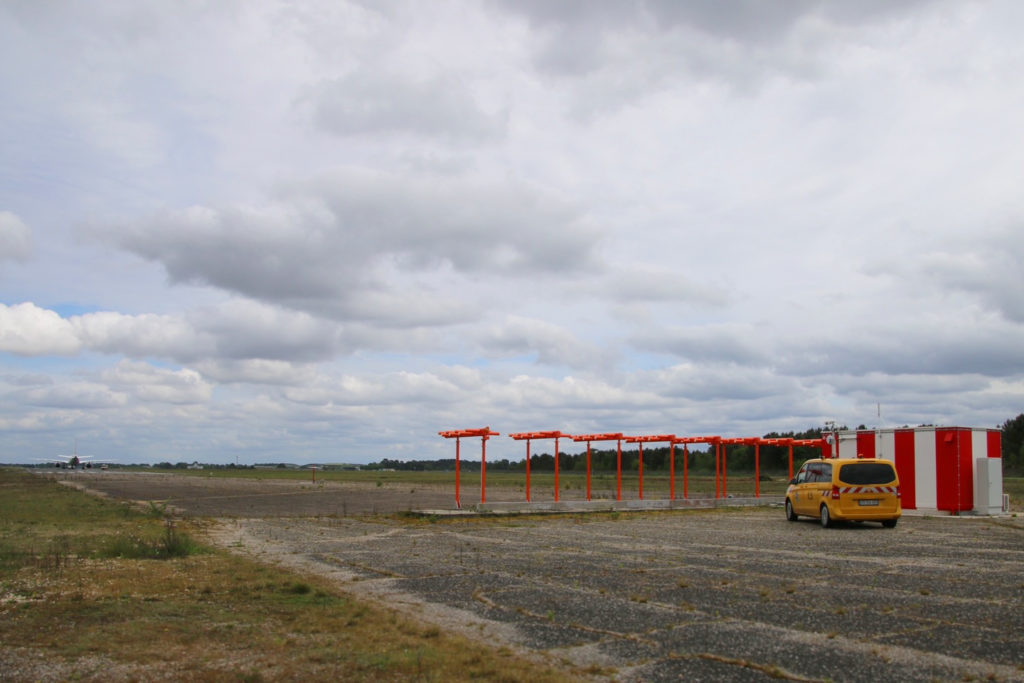
The ICAO, the International Civil Aviation Organization, recommends systematically and periodically checking, in flight and on the ground, these ILS in order to meet maximum safety requirements. The DGAC has chosen to equip itself with two calibration planes and vehicles, equipped with numerous tools and measuring devices, some with GNSS receivers. These vehicles are essential for air traffic control technical services and complement aircraft navigation equipment, comprising GNSS positioning and conventional radio aids. This type of vehicle is now used at all major airports in France.
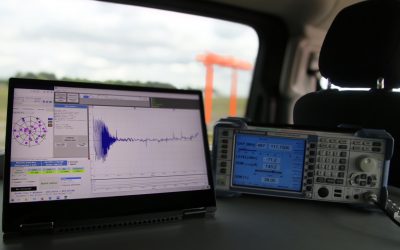
Controlling and certifying an ILS requires measuring its radioelectric emission while mastering the positioning of the vehicle for each measurement sample. Cameras and lasers on board these vehicles were used, but these positions lacked precision, did not ensure perfect reproducibility and could pose reliability concerns. The measurements must be made on the runway and require an interruption of air traffic. A reliable and efficient position solution contributes to the quality and speed requirements of measurements during these critical phases of intervention.

The DGAC’s calibration planes have been equipped for several decades with a differential GPS system designed specifically for this use, coupled with a ground beacon deposited during each calibration. The DGAC wanted to equip these vehicles with similar systems to improve measurements on the ground while controlling costs.
Cadden was chosen to equip the vehicles with Trimble Intech GNSS receivers and the ABX-TWO model was chosen for this project.
GNSS on board vehicles is useful in qualifying ILS measurements, correcting the trajectory and monitoring position deviations. Connected to the ILS receiver, it makes it possible to acquire the ILS measurements (level of fields, frequency, modulation, distortions, etc.) and GPS values (position and time) in one go. For the DGAC, this is a real saving of time and quality assurance to meet the requirements of their profession.


Mentions légales – Politique de données personnelles – ©CADDEN
Vos données sont collectées et traitées pour vous envoyer notre newsletter et améliorer l’expérience utilisateur du site web. Dans ce cadre, le responsable du traitement est CADDEN. Vous disposez d’un droit d’accès, de rectification, et de suppression de vos données, ainsi que d’un droit de limitation, de portabilité ou d’opposition. Pour exercer ces droits, vous pouvez nous contacter via le formulaire de contact. Pour plus d’informations sur la façon dont nous traitons vos données personnelles, vous pouvez consulter notre Politique de confidentialité.